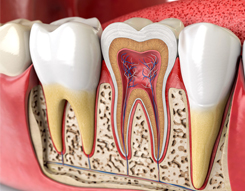
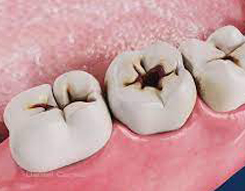
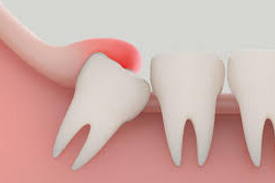
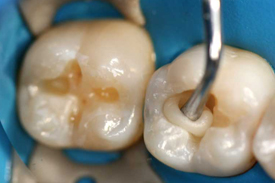
Dental caries, also known as tooth decay or a cavity, is an infection, bacterial in origin, that causes demineralization and destruction of the hard tissues of the teeth (enamel, dentin and cementum). It is a result of the production of acid by bacterial fermentation of food debris accumulated on the tooth surface.If demineralization exceeds saliva and other remineralization factors such as from calcium and fluoridated toothpastes, these once hard tissues progressively break down, producing dental caries (cavities, holes in the teeth). Today, caries remain one of the most common diseases throughout the world. Cariology is the study of dental caries.
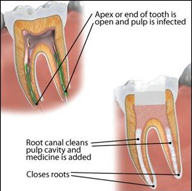
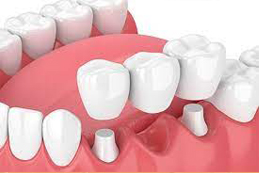
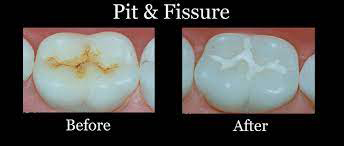
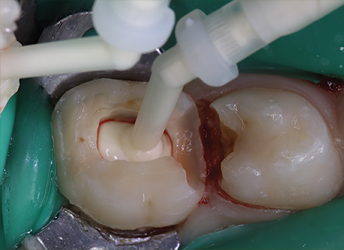
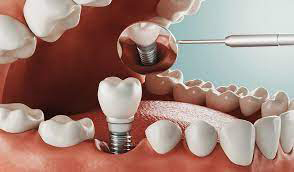
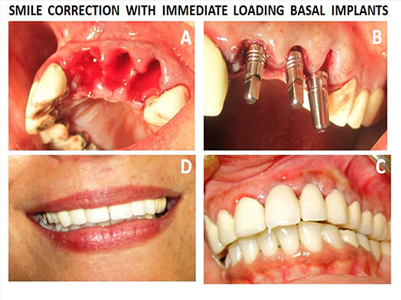
Depending on the extent of tooth destruction, various treatments can be used to restore teeth to proper form, function, and aesthetics, but there is no known method to regenerate large amounts of tooth structure. Instead, dental health organizations advocate preventive and prophylactic measures, such as regular oral hygiene and dietary modifications, to avoid dental caries